
Trong bài viết này, chúng ta sẽ cùng tìm hiểu một ví dụ về Spring ORM sử dụng Hibernate và JPA để quản lý transaction. Ta sẽ đi qua một ví dụ rất đơn giản về ứng dụng Spring với các tính năng:
- Dependency Injection (tiêm phụ thuộc) với @Autowired
- JPA EntityManager (cung cấp bởi Hibernate)
- Phương thức giao dịch dùng annotation (@Transactional)
Một project Spring ORM mẫu
Trong ví dụ này, ta sử dụng database trong bộ nhớ (in-memory). Vì vậy bạn không cần phải cài đặt bất kỳ database nào (nhưng bạn có thể thay đổi sang một database khác trong mục datasource của file spring.xml).
Đây là một ứng dụng Spring ORM chạy riêng lẻ để tối giản các dependency (phụ thuộc). Nhưng bạn luôn có thể dễ dàng chuyển đổi nó thành một dự án web hoàn chỉnh bằng cách cấu hình nó nếu bạn đã quen thuộc với Spring.
Trước hết, hãy cùng xem xét từng thành phần của dự án.
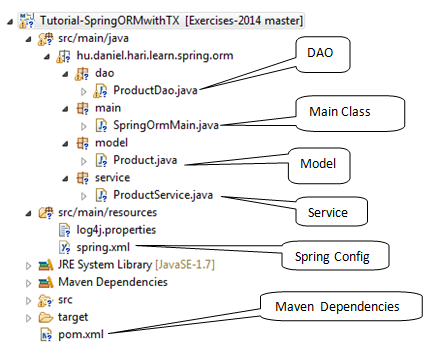
Các dependency Maven
Dưới đây là file pom.xml cuối cùng chứa các dependency cho Spring ORM. Trong ví dụ này, chúng ta sử dụng Spring 4 và Hibernate 4.
<project xmlns="<https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0>" xmlns:xsi="<https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance>" xsi:schemaLocation="<https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0> <https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd>">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>hu.daniel.hari.learn.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>Tutorial-SpringORMwithTX</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<properties>
<!-- Generic properties -->
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<java.version>1.7</java.version>
<!-- SPRING & HIBERNATE / JPA -->
<spring.version>4.0.0.RELEASE</spring.version>
<hibernate.version>4.1.9.Final</hibernate.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- LOG -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- JPA Vendor -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-entitymanager</artifactId>
<version>${hibernate.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- IN MEMORY Database and JDBC Driver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>hsqldb</groupId>
<artifactId>hsqldb</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0.7</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>${java.version}</source>
<target>${java.version}</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
- Chúng ta cần
spring-contextvàspring-ormlàm các dependency của Spring. - Ta sử dụng
hibernate-entitymanagercho Hibernate với vai trò là một triển khai của JPA. Nó phụ thuộc vàohibernate-core, đó là lý do chúng ta không cần khai báohibernate-coremột cách tường minh trong filepom.xml. Nó sẽ được tải về dự án của chúng ta thông qua cơ chế bắc cầu dependency (transitive dependency) của Maven. - Chúng ta cũng cần dependency cho JDBC driver để truy cập database. Ở đây, ta sử dụng HSQLDB, vốn đã bao gồm cả JDBC driver và một database trong bộ nhớ có thể hoạt động ngay.
Model class
Chúng ta có thể sử dụng các annotation JPA tiêu chuẩn để map (ánh xạ) trong các model bean vì Hibernate cung cấp sẵn một triển khai của JPA.
package hu.daniel.hari.learn.spring.orm.model;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class Product {
@Id
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Product() {
}
public Product(Integer id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Product [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}
Chúng ta sử dụng các annotation @Entity và @Id của JPA để định danh POJO của ta là một Entity và để xác định khóa chính cho nó.
Class DAO
Chúng ta tạo một class DAO rất đơn giản cung cấp các method persist và findAll.
package hu.daniel.hari.learn.spring.orm.dao;
import hu.daniel.hari.learn.spring.orm.model.Product;
import java.util.List;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContext;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class ProductDao {
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager em;
public void persist(Product product) {
em.persist(product);
}
public List<Product> findAll() {
return em.createQuery("SELECT p FROM Product p").getResultList();
}
}
@Componentlà một annotation của Spring, cho Spring container biết rằng chúng ta có thể sử dụng class này thông qua Spring IoC (Dependency Injection).- Chúng ta sử dụng annotation
@PersistenceContextcủa JPA để yêu cầu dependency injection mộtEntityManager. Spring sẽ inject (chèn) một thực thểEntityManagerphù hợp dựa theo cấu hình trongspring.xml.
Class service
Class service đơn giản của chúng ta có 2 method ghi và 1 method đọc:- add, addAll và listAll.
package hu.daniel.hari.learn.spring.orm.service;
import hu.daniel.hari.learn.spring.orm.dao.ProductDao;
import hu.daniel.hari.learn.spring.orm.model.Product;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Component
public class ProductService {
@Autowired
private ProductDao productDao;
@Transactional
public void add(Product product) {
productDao.persist(product);
}
@Transactional
public void addAll(Collection<Product> products) {
for (Product product : products) {
productDao.persist(product);
}
}
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public List<Product> listAll() {
return productDao.findAll();
}
}
- Chúng ta sử dụng annotation
@Autowiredcủa Spring để injectProductDaovào class service. - Vì ta muốn sử dụng quản lý transaction, các method được đánh dấu bằng annotation
@Transactionalcủa Spring. MethodlistAllchỉ đọc database, vì vậy chúng ta đặt annotation@Transactionalở chế độ chỉ đọc (read-only) để tối ưu hóa nó.
File cấu hình bean
Khi đã có đủ các class Java cho dự án ví dụ, tiếp theo ta sẽ xem qua file cấu hình Spring bean spring.xml.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="<https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans>"
xmlns:p="<https://www.springframework.org/schema/p>"
xmlns:context="<https://www.springframework.org/schema/context>"
xmlns:tx="<https://www.springframework.org/schema/tx>"
xmlns:xsi="<https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance>"
xsi:schemaLocation="
<https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans>
<https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd>
<https://www.springframework.org/schema/context>
<https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd>
<https://www.springframework.org/schema/tx>
<https://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd>
">
<!-- Scans the classpath for annotated components that will be auto-registered as Spring beans -->
<context:component-scan base-package="hu.daniel.hari.learn.spring" />
<!-- Activates various annotations to be detected in bean classes e.g: @Autowired -->
<context:annotation-config />
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:hsqldb:mem://productDb" />
<property name="username" value="sa" />
<property name="password" value="" />
</bean>
<bean id="entityManagerFactory"
class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean"
p:packagesToScan="hu.daniel.hari.learn.spring.orm.model"
p:dataSource-ref="dataSource"
>
<property name="jpaVendorAdapter">
<bean class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaVendorAdapter">
<property name="generateDdl" value="true" />
<property name="showSql" value="true" />
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- Transactions -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager">
<property name="entityManagerFactory" ref="entityManagerFactory" />
</bean>
<!-- enable the configuration of transactional behavior based on annotations -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" />
</beans>
- Đầu tiên, chúng ta cho Spring biết rằng ta muốn sử dụng cơ chế quét classpath (classpath scanning) cho các thành phần Spring (Service, DAO) thay vì phải định nghĩa từng bean một trong file XML. Chúng ta cũng đã kích hoạt việc nhận diện annotation của Spring.
- Thêm datasource, hiện tại là database trong bộ nhớ HSQLDB.
- Chúng ta thiết lập một JPA
EntityManagerFactoryđể ứng dụng sử dụng để lấy mộtEntityManager. Spring hỗ trợ 3 cách khác nhau để thực hiện việc này, và ở đây chúng ta đã sử dụngLocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBeanđể có đầy đủ các tính năng của JPA. Chúng ta thiết lập các thuộc tính của nó như sau:- Thuộc tính
packagesToScantrỏ đến package chứa các model class của chúng ta. datasourceđã được định nghĩa trước đó trong file cấu hình Spring.jpaVendorAdapterlà Hibernate và được thiết lập một số thuộc tính cho Hibernate.
- Thuộc tính
- Chúng ta tạo một thực thể
PlatformTransactionManagercủa Spring dưới dạngJpaTransactionManager. Loại transaction manager (quản lý giao dịch) này phù hợp cho các ứng dụng sử dụng mộtEntityManagerFactoryduy nhất của JPA để truy cập dữ liệu. - Chúng ta kích hoạt việc cấu hình hành vi transaction dựa trên annotation, và thiết lập
transactionManagermà chúng ta vừa tạo.
Chương trình kiểm thử
Sau khi có một ví dụ hoàn chỉnh, giờ ta sẽ viết một chương trình để kiểm thử nó.
public class SpringOrmMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create Spring application context
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:/spring.xml");
//Get service from context. (service's dependency (ProductDAO) is autowired in ProductService)
ProductService productService = ctx.getBean(ProductService.class);
//Do some data operation
productService.add(new Product(1, "Bulb"));
productService.add(new Product(2, "Dijone mustard"));
System.out.println("listAll: " + productService.listAll());
//Test transaction rollback (duplicated key)
try {
productService.addAll(Arrays.asList(new Product(3, "Book"), new Product(4, "Soap"), new Product(1, "Computer")));
} catch (DataAccessException dataAccessException) {
}
//Test element list after rollback
System.out.println("listAll: " + productService.listAll());
ctx.close();
}
}
Bạn có thể thấy chúng ta có thể khởi động Spring container từ một method main dễ dàng như thế nào. Chúng ta đang lấy entry point (điểm đầu vào) đầu tiên được inject dependency, đó là thực thể của class service.
Tham chiếu của class ProductDao được inject vào class Client sau khi spring context được khởi tạo. Sau khi có được thực thể productService, chúng ta có thể kiểm thử các method của nó. Mọi lời gọi method sẽ đều có tính chất transactional (giao dịch) nhờ vào cơ chế proxy của Spring. Trong ví dụ này, chúng ta cũng kiểm thử cả chức năng rollback (đưa hệ thống hoặc dữ liệu về lại trạng thái ổn định trước đó).
Nếu bạn chạy chương trình kiểm thử trên, bạn sẽ nhận được log như dưới đây.
Hibernate: insert into Product (name, id) values (?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into Product (name, id) values (?, ?)
Hibernate: select product0_.id as id0_, product0_.name as name0_ from Product product0_
listAll: [Product [id=1, name=Bulb], Product [id=2, name=Dijone mustard]]
Hibernate: insert into Product (name, id) values (?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into Product (name, id) values (?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into Product (name, id) values (?, ?)
Hibernate: select product0_.id as id0_, product0_.name as name0_ from Product product0_
listAll: [Product [id=1, name=Bulb], Product [id=2, name=Dijone mustard]]
Lưu ý rằng transaction thứ hai đã được rollback, đó là lý do tại sao danh sách sản phẩm không thay đổi. Nếu bạn sử dụng file log4j.properties từ code đính kèm, bạn có thể thấy những gì đang diễn ra ở bên trong ứng dụng.
Bạn có thể tải về dự án ví dụ Spring ORM hoàn chỉnh từ liên kết này và thử nghiệm thêm để tìm hiểu sâu hơn về các ứng dụng dạng này.
 6 phút để đọc
6 phút để đọc
