Spring Bean Scope cho phép quản lý chặt chẽ quá trình tạo các instance của bean. Đôi khi bean được khởi tạo dưới dạng singleton, nhưng trong những tình huống khác có thể cần tạo một instance mới cho mỗi request hoặc mỗi session.

Bean scope trong Spring
Có 5 loại scope của Spring Bean:
singleton: Chỉ có 1 instance của bean được tạo trong container Spring. Đây là scope mặc định. Khi dùng scope này, cần đảm bảo bean không có biến chia sẻ để tránh lỗi dữ liệu không nhất quán.prototype: Mỗi lần bean được yêu cầu từ container Spring sẽ tạo ra một instance mới.request: Tương tự prototype, nhưng dùng cho ứng dụng web. Bean mới sẽ được tạo cho mỗi HTTP request.session: Bean mới sẽ được tạo cho mỗi HTTP session.global-session: Dùng cho ứng dụng Portlet để tạo global session bean.
Spring Bean Singleton và Prototype Scope
Hai scope singleton và prototype có thể dùng trong ứng dụng Spring độc lập. Chúng ta có thể dễ dàng cấu hình bằng annotation @Scope.
Giả sử có lớp Java Bean sau:
package com.journaldev.spring;
public class MyBean {
public MyBean() {
System.out.println("MyBean instance created");
}
}
Tiếp theo định nghĩa lớp cấu hình Spring, trong đó khai báo phương thức để lấy instance MyBean từ spring container.
package com.journaldev.spring;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
@Configuration
public class MyConfiguration {
@Bean
@Scope(value="singleton")
public MyBean myBean() {
return new MyBean();
}
}
Lưu ý, singleton là scope mặc định nên chúng ta có thể bỏ @Scope(value="singleton") khỏi định nghĩa bean ở trên. Tiếp theo, tạo phương thức main và kiểm thử scope singleton.
package com.journaldev.spring;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class MySpringApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
ctx.register(MyConfiguration.class);
ctx.refresh();
MyBean mb1 = ctx.getBean(MyBean.class);
System.out.println(mb1.hashCode());
MyBean mb2 = ctx.getBean(MyBean.class);
System.out.println(mb2.hashCode());
ctx.close();
}
}
Sau khi thực thi chương trình trên, chúng ta sẽ nhận được kết quả như sau:
MyBean instance created
867988177
867988177
Cả 2 instance có cùng hashcode, constructor chỉ gọi 1 lần, nghĩa là container Spring luôn trả về cùng một instance.
Nếu thay scope thành prototype:
@Bean
@Scope(value="prototype")
public MyBean myBean() {
return new MyBean();
}
Lần này khi phương thức main được thực thi, kết quả đầu ra sẽ như sau.
MyBean instance created
867988177
MyBean instance created
443934570
Rõ ràng là instance của MyBean được tạo ra mỗi khi nó được yêu cầu từ spring container. Bây giờ hãy thay đổi scope thành request.
@Bean
@Scope(value="request")
public MyBean myBean() {
return new MyBean();
}
Trong trường hợp này, chúng ta sẽ nhận được ngoại lệ sau:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException: No Scope registered for scope name 'request'
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:347)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.getBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:224)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.resolveNamedBean(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:1015)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBean(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:339)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBean(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:334)
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.getBean(AbstractApplicationContext.java:1107)
at com.journaldev.spring.MySpringApp.main(MySpringApp.java:12)
Điều này xảy ra vì các scope request, session và global-session không khả dụng cho các ứng dụng standalone.
Spring Bean Request và Session Scope
Để minh họa scope request và session, chúng ta sẽ tạo ứng dụng Spring Boot web.
Tạo project Spring Boot Starter với module web để chạy ứng dụng web.
Spring Boot Starter Project với Spring Bean Scopes
Cấu trúc cuối cùng của project sẽ giống như hình bên dưới.
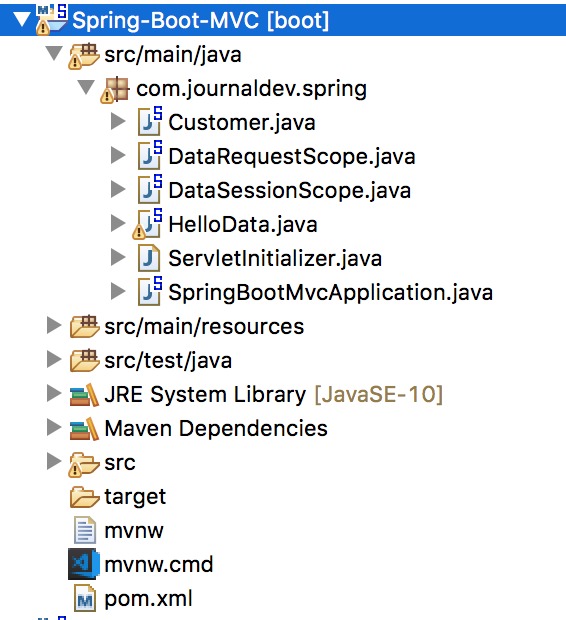
Cấu trúc project Spring Bean Scopes Spring Boot Web App
ServletInitializer và SpringBootMvcApplication là các lớp được tạo tự động của Spring Boot, không cần chỉnh sửa. Dưới đây là tệp pom.xml với các dependencies cần thiết cho ứng dụng (tệp này có thể hơi khác đôi chút tùy phiên bản Eclipse).
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="<https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0>" xmlns:xsi="<https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance>"
xsi:schemaLocation="<https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0> <https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd>">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.journaldev.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>Spring-Boot-MVC</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>Spring-Boot-MVC</name>
<description>Spring Beans Scope MVC</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>10</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Tạo một số thành phần Spring và cấu hình chúng thành các bean của Spring trong Spring container, với scope là request và session.
Spring Bean Request Scope
package com.journaldev.spring;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ScopedProxyMode;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Scope(value = "request", proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS)
public class DataRequestScope {
private String name = "Request Scope";
public DataRequestScope() {
System.out.println("DataRequestScope Constructor Called");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
Spring Bean Session Scope
package com.journaldev.spring;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ScopedProxyMode;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Scope(value = "session", proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS)
public class DataSessionScope {
private String name = "Session Scope";
public DataSessionScope() {
System.out.println("DataSessionScope Constructor Called at "+LocalDateTime.now());
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
Spring Component
Kế tiếp tạo một Spring component và dùng Spring để tự động cấu hình các bean ở trên.
package com.journaldev.spring;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Customer {
@Autowired
private DataRequestScope dataRequestScope;
@Autowired
private DataSessionScope dataSessionScope;
public DataRequestScope getDataRequestScope() {
return dataRequestScope;
}
public void setDataRequestScope(DataRequestScope dataRequestScope) {
this.dataRequestScope = dataRequestScope;
}
public DataSessionScope getDataSessionScope() {
return dataSessionScope;
}
public void setDataSessionScope(DataSessionScope dataSessionScope) {
this.dataSessionScope = dataSessionScope;
}
}
Spring Rest Controller
Cuối cùng, tạo một lớp RestController và cấu hình một số endpoint API để phục vụ mục đích kiểm thử.
package com.journaldev.spring;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloData {
@Autowired
private Customer customer;
@RequestMapping("/nameRS")
public String helloRS() {
return customer.getDataRequestScope().getName();
}
@RequestMapping("/nameSSUpdated")
public String helloSSUpdated() {
customer.getDataSessionScope().setName("Session Scope Updated");
return customer.getDataSessionScope().getName();
}
@RequestMapping("/nameSS")
public String helloSS() {
return customer.getDataSessionScope().getName();
}
}
Cấu hình Session Timeout trong Spring Boot
Cuối cùng, cần cấu hình các biến timeout cho session trong Spring Boot, thêm các thuộc tính dưới đây vào tệp src/main/resources/application.properties.
server.session.cookie.max-age= 1
server.session.timeout= 1
Bây giờ các Spring bean với scope session sẽ bị vô hiệu sau 1 phút. Chạy lớp SpringBootMvcApplication như một ứng dụng Spring Boot. Bạn sẽ thấy đầu ra dưới đây cho các endpoint được cấu hình.
2018-05-23 17:02:25.830 INFO 6921 --- [main] s.w.s.m.m.a.RequestMappingHandlerMapping : Mapped "{[/nameRS]}" onto public java.lang.String com.journaldev.spring.HelloData.helloRS()
2018-05-23 17:02:25.831 INFO 6921 --- [main] s.w.s.m.m.a.RequestMappingHandlerMapping : Mapped "{[/nameSSUpdated]}" onto public java.lang.String com.journaldev.spring.HelloData.helloSSUpdated()
2018-05-23 17:02:25.832 INFO 6921 --- [main] s.w.s.m.m.a.RequestMappingHandlerMapping : Mapped "{[/nameSS]}" onto public java.lang.String com.journaldev.spring.HelloData.helloSS()
Kiểm thử Spring Bean Request Scope
Mở trình duyệt và truy cập https://localhost:8080/nameRS. Console sẽ in thông điệp DataRequestScope Constructor Called ở mỗi request.
Kiểm thử Spring Bean Session Scope
Truy cập https://localhost:8080/nameSS và bạn sẽ nhận được kết quả sau.
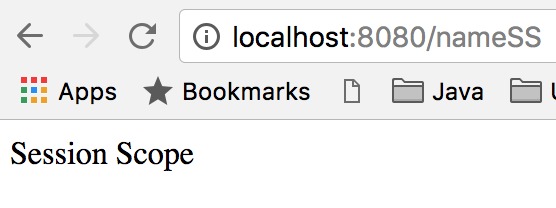
Kết quả kiểm thử Session Scope
Bây giờ truy cập https://localhost:8080/nameSSUpdated để giá trị name của DataSessionScope được cập nhật thành Session Scope Updated.
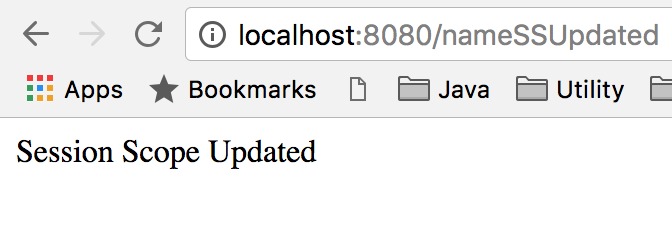
Kết quả cập nhật giá trị của Session Scope
Tiếp theo, truy cập lại https://localhost:8080/nameSS và bạn sẽ thấy giá trị đã được cập nhật.
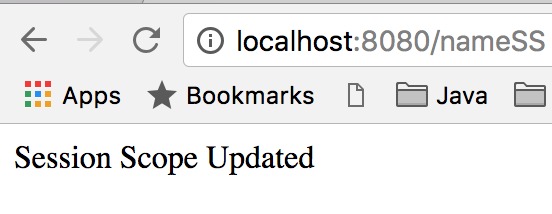
Hiển thị giá trị đã cập nhật của Session Scope
Lúc này, trong console chỉ hiển thị DataSessionScope Constructor Called at XXX một lần duy nhất.
Bây giờ hãy chờ 1 phút để bean có scope session bị vô hiệu. Sau đó, truy cập lại https://localhost:8080/nameSS và bạn sẽ thấy giá trị ban đầu. Đồng thời, hãy kiểm tra console để thấy thông báo tạo mới DataSessionScope của container.

Bean Session được khởi tạo lại sau khi hết hạn
Đó là toàn bộ phần hướng dẫn về Spring Bean Scopes.
Bạn có thể tải project Spring Beans Scope Spring Boot từ GitHub Repository.
 6 phút để đọc
6 phút để đọc
