Every time people discuss blockchain, they mention the advanced security of smart contracts as the backbone of the technology. However, what is a smart contract – to be exact?
If you still have this question in mind, you should keep our article through. Here we discuss smart contracts in very detail and in an easy-to-understand way.
Scroll down now!
What Is a Smart Contract?

Since smart contracts are the critical pillar of blockchain, it is helpful first to understand how a blockchain works.
Blockchain is an immutable decentralized ledger that allows digitalizing assets and anything of value into blocks of information and sharing it among permissioned network members without the intervention of third parties and legal framework. The information in the chain can be added, yet unchangeable.
As mentioned above, a blockchain is decentralized, making transactions quicker, cheaper, and more transparent.
Check later: What is blockchain?
Then, who controls and runs the chain instead of humans? – It is a smart contract!
Smart contracts are smart and automated contracts that contain pre-determined conditions knowns as terms for designed functions. If all conditions are met, smart contracts approve the transactions. Otherwise, they will refuse any breaches of said conditions and protect participants from damages.
How Does A Smart Contract Work?
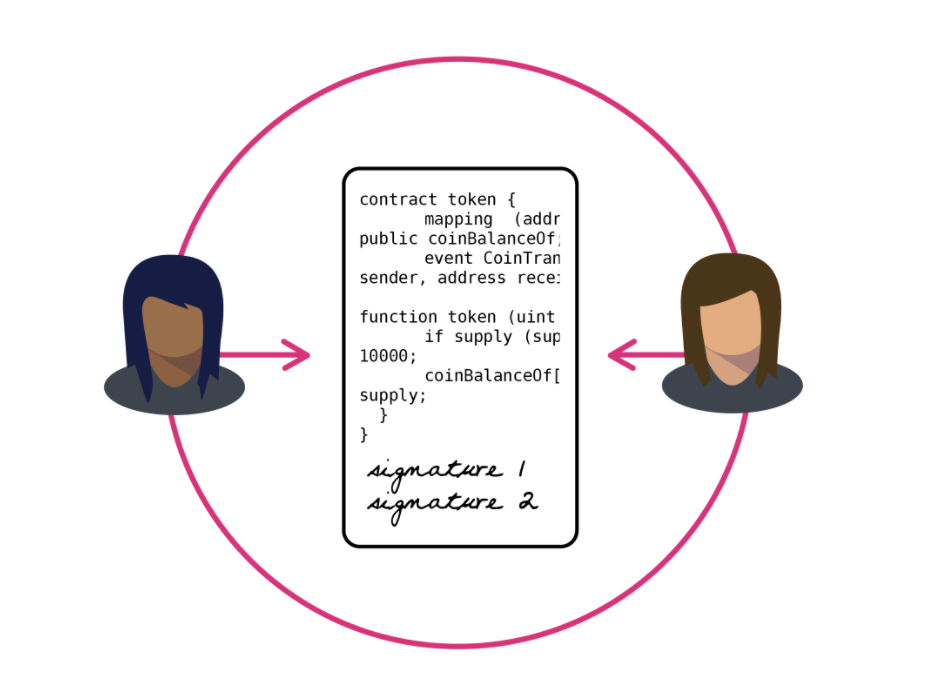
Here is a simple example of a smart contract.
A restaurant uses blockchain to facilitate customers’ payments. There is a term in their delivery policy that customers will get their money back if the delivery is longer than 20 minutes.
- First, the developer writes a slab of code spelling out that policy and pushes the smart contract to a blockchain network, such as Ethereum, to enforce the contract.
- Then, the restaurant will invite their customers to the blockchain, which allows them to create their wallets and exchange cryptocurrencies to make payments later.
- Next time, a customer places an order and puts a fund in escrow as payment. The restaurant will also put the delivery status information in the chain. If the information is within 20 minutes, the smart contract releases the fund from the escrow to the restaurant account. In contrast, the fund will be returned to the customer.
A smart contract usually does not work alone in the real world. It works with other smart contracts to complete complicated transactions. Nonetheless, the process is similar.
Benefits of Smart Contracts in a Blockchain
As simple as a smart contract works, it benefits the economy significantly.
Trust and Transparency
Blockchains and smart contracts work on a zero-trust principle.
Participants might not know each other while making the transactions. Yet, they will be aware and have a record whenever there is new information at the same time throughout the contract’s life.
The data is immutable with no involved third parties; thus, smart contracts eliminate the fear of information being altered for malicious purposes.
Autonomy and Accuracy
When large contracts depend on human intervention to fulfill numerous conditions, things can go wrong.
At that time, businesses risk losing money to correct human errors and even getting involved in a drawn-out legal issue.
Smart contracts help parties to automate transactions independently and reduce risks.
Reduction of Cost and Time
Getting rid of intermediaries saves businesses a lot of transactions and fixing costs. There are also fewer associated back-office expenditures.
In addition, smart contracts reduce the time of sharing data and informing changes within the network.
And time is money.
Limitations of Smart Contracts in a Blockchain

Although smart contracts are not new, they have only developed significantly recently. Thus, there is room for improvement.
Security Vulnerabilities
Smart contracts are supposed to be hack-proof.
However, developers might write insecure code in the first place and leave major security flaws and vulnerabilities for hackers to attack the smart contracts and data in the blockchain.
Unfortunately, businesses often do not pay enough attention to smart auditing contracts.
Must-read: Top practices of smart contract auditing.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Once smart contracts are in the blockchain, participants cannot change the rules. It is often challenging if parties decide to change the terms of their agreements.
Thus, we often do not recommend smart contracts for relational contracts, which requires room for flexibility.
Legal Ramifications
A benefit of smart contracts is to eliminate the requirements for legal frameworks. However, it can also be a disadvantage when there is a loss or dispute.
Businesses must be well-aware of exceptions or possible damages to prevent unexpected situations.
7+ Common Applications of Smart Contracts
Weighing the pros and cons, we confirm that smart contracts are still very promising and beneficial. As a result, they have been applied to more and more aspects of the economy and society.
- Recordings
Blockchain allows the recording of significant data at high speed and security. This is an enormous benefit in medicine and the healthcare industry regarding diagnosing and curing patients.
- Financial transactions
Smart contracts are common in facilitating a huge amount of funds and savings within the community rather than going to traditional banks or other financial parties. They help fasten the approval flows and calculations in real-time.
- Legal contracts
Usually, businesses use smart contracts to verify the payment of contracts based on specific triggering events and impose penalties accordingly.
- Real-estate property ownership
Paperwork related to transferring property ownership is a real pain in the real estate industry. Thankfully, smart contracts can digitalize property ownership, such as lands, buildings, and assets – ready to be traded.
- Voting
It costs millions of dollars to organize a voting event. Yet, allegations of voting fraud have become increasingly common, and which cost another million to investigate the scam and re-organize the voting.
- DAO governance
A decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) often runs without central leadership, meaning that a community makes decisions from the bottom up according to smart contracts.
- Non-fungible tokens (NFTs)
Smart contracts serve as a tool to carry out a sale agreement on a fundamental level to transfer or sell non-fungible tokens (NFTs)
Final Thoughts
If you decide to use blockchains for your businesses, it is better to spend an enormous amount of time investigating their principles, including smart contracts and how a smart contract works.
Thus, do not skip our series on this topic!
 5 minutes read
5 minutes read
