
Blockchain is a relatively recent innovation that gained widespread recognition primarily following the global surge in interest surrounding Cryptocurrency and Bitcoin. When reading this, you might also be interested in understanding what blockchain is, its operational mechanics, and most importantly – is blockchain secure?
What Is Blockchain Technology?

Introduced in 1991, blockchain is a distributed ledger or database to store and secure digital data, giving access to several parties simultaneously.
Those parties provide information together, known as a record or a block. The information cannot be modified. Each has a unique hash and a specific storage capacity. Once the block is fully packed with data, it is set in stone and linked to others via cryptography to form a chain of records – called “blockchain” for short.
According to IBM, there are five significant benefits of blockchain that every investor and researcher should know:
- Enhanced security
Since your data is crucial and sensitive, managing how such information is viewed is essential. Thus, you wonder: is Blockchain secure?
Blockchain allows the creation of a record of data that is encrypted end-to-end. The record cannot be altered or deleted. When you share the blockchain, other parties given permission can view the information and add new blocks to the chain.
In addition, data is stored across nodes of a computer network instead of a single vulnerable server. Hackers find it challenging to access your sensitive information, let alone cause fraud or unauthorized activities.
Even if someone tries to alter the data at one instance, other notes are not affected; thus, it deters that actor from doing bad things.
- Better transparency
Organizations must keep their separate databases without using blockchain and share them with other parties. It takes time and effort to update stakeholders if there is a change.
Blockchain, however, uses a distributed ledger to display data recorded in multiple locations in one place. Each transaction is stamped with time and date and immutably recorded.
It means all participants have access to view the same data at the same time. They are possible to check the history of transaction and detect suspicious frauds.
- Immediate traceability
Thanks to its transparency, blockchain provides an instant audit trail for an asset.
For example, when customers desire to know about human rights or environmental issues related to your product. The blockchain serves as a provenance proof and traceability data to be directly shared with customers to enhance their trust.
- Improved efficiency and speed
Blockchain eliminates the time-consuming, paper-heavy processes that usually require the mediation of third parties. Updating papers or reconciling multiple ledgers regarding documentation or data exchanges are unnecessary. Instead, the technology streamlines data and fastens transactions.
- Automated smart contracts
Contracts between parties are created and stored in a blockchain with many predetermined conditions. When one condition is met, the next step in the workflow is triggered automatically.
For instance, if a customer provides all required files to a claim, the claim is settled and paid. All participants are up-to-date on specific outcomes with fewer human interventions.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Some buzzwords
Blockchain uses two crucial concepts: blocks and nodes.
- Blocks: As mentioned above, a block is a set of information (data) recorded by parties. Each block is generated with a random and unique 32-bit whole number known as a nonce. The nonce, then, generates its 256-bit number called a cryptographic hash. After that, the data is signed and tightened with such nonce and hash until the block is mined.
- Nodes: Nodes are electronic devices added to the network to connect the blockchain. Each node features its blockchain copy. Then, they run special software to validate the transactions within the chain and store the complete history on the network.
A Typical Process in Blockchain
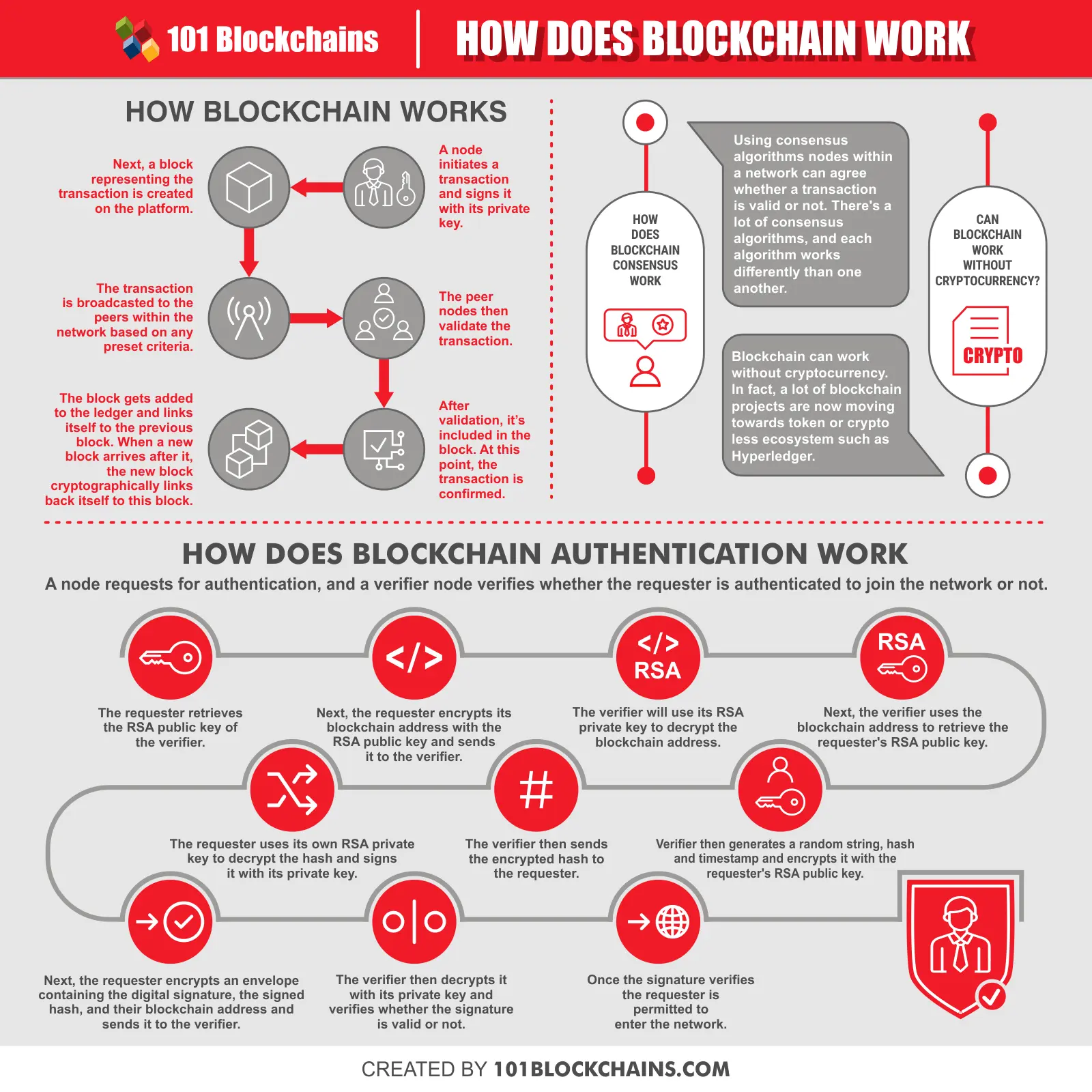
There are usually six steps to add a block to the chain:
- Firstly, a transaction of data value, validations, relevant rules, etc., is initiated at a node and signed with a private key.
- Next, a block to present the translation information is usually created by a flooding protocol.
- Based on predetermined conditions, verifying nodes are broadcasted about the transaction, and a new block is ready to validate the data.
- The validation is based on preset criteria.
- Supposing that the transaction is authentic and confirmed, the containing block will get a place in the ledger with its timestamp to secure it from alteration.
- Finally, the newly-created block links itself to the previous block, creating a hash pointer in the chain.
Is Blockchain Secure?
If you ask, is blockchain secure? Then Yes, blockchain is secure in its principle.
Each block has its unique 32-bit nonce and 256-bit hash numbers. Thus, if a hacker wants to change its entry, they have to calculate around four billion nonce-and-harsh combinations for the block itself and other billions of calculations for its subsequent block.
This is almost impossible unless the hacker does faster than other nodes or has more powerful computers than all other nodes combined. Otherwise, such an alteration is rejected by other nodes automatically.
So much a theory. People still make countless efforts to hack the chain. One in a trillion, they combine a correct nonce and harsh. Plus, hackers might use a node’s communications or wallets to save private keys. Many other ways.
You had better be safe than sorry by investing in cybersecurity.
Common Blockchain Risks

Hackers Risk
Hackers are those working on a block to find a nonce and its accepted hash to access the chain and steal its sensitive information. In 2019 alone, there were twelve crypto-related exchanges hacked.
Here are several ways your blockchain is vulnerable to hackers.
- The hackers might work with a large group of miners to take control of half the network.
- The hackers might send you bogus emails to steal your necessary credentials on online wallet apps. Even “cold” hardware wallets disconnected from the internet might be prime targets.
- An eclipse attack is another possible risk. Miners and hackers know that nodes within a blockchain network remain in constant communication. Then, they send false data to trick the nodes and access real-time data routed in between.
No Human Safeguards
Blockchain automatically validates and executes transactions. There is hardly any manual intervention.
Although this technology offers advances for guaranteeing the authenticity of the identity or information included in the block, it is utterly unconcerned with the sender and receiver. It is possible now that blockchain application – such as bitcoin or other cryptos, is used by criminals to circumvent their illegal money laundering.
Expensive and Unsecure Decentralization
Blockchain is costly to maintain the networks and run the function.
For instance, blockchain technology requires special software which is expensive to develop, get correct, and operate. The amount of electricity consumption used to do the calculations is vast. It was estimated that the total energy of the bitcoin network was equivalent to the electricity for two million U.S. homes.
Such decentralization is extremely expensive.
Permissioned and Permissionless Chains
Permissioned, so-called private blockchains are more secure since they request a privileged invitation to join and restrict outsiders.
Permissionless, so-called public blockchains are available for anyone to make a transaction without control. Data are mined, copied, and stored on nodes worldwide. Bitcoin, Dash, and Litecoin are examples.
Possible Loss of Identities
A “private key” is a vital piece of data on the blockchain network used to approve outgoing transactions. Anyone aware of this key may use the related funds.
If your private key is stolen for any reason, other people can also lose control of the blockchain.
This risk occurs quite frequently. Many investors wonder why many bitcoins were suddenly frozen for all of the eternity one day. It is possible that the owner of the coins has already lost the important key.
Recommended Blockchain Security Practices
From all information above, blockchain is not entirely risk-free. Thus, it would be beneficial if you never let your guard down.
We have some security practices to help:
System selection
Ensure a private blockchain is established and deployed on a reliable, secure system. Poorly chosen underlying technologies for business requirements and procedures can expose data security threats due to their flaws.
Identity and access management
It’sIt’s crucial to keep in mind three distinct actors to identify: owners, issuers, and verifiers. Personal credentials for an identity owner may be issued by the identity issuer, a reliable third party such as the local government. The identity issuer certifies the accuracy of the personal information contained in the credential by issuing it. The identity holder can keep such credentials in their own identity wallet and utilize them later to support claims made to a third party about their identity.
Once you identify important participants, only send the access information to them.
Key management
Online or hardware wallets are still a preferable way to save your private keys. However, not all wallets are secure enough.
You must choose wallets from trusted brands, such as Hardware-Security-Modules (HSM) for hardware storage or Locker.io for online key management.
Your Takeaway
Is blockchain secure? Yes, the technology is confident but not wholly immune to hacking activities. Strictly follow blockchain security practices to protect your key and your block.
You can contact us to speak with blockchain security experts and seek guidance if you still have questions.
 7 minutes read
7 minutes read
