Advanced technologies are like a double-edged sword. While they revolutionize our life and how we do business, technologies also expose us to higher cyber attacks. Thus, it is important to always update yourself on the latest trends of cyber threats and, more importantly, how to prevent or minimize the damages.
This year, IBM published its IBM Security X-Force Threat Intelligence Index report to alert individuals and businesses against news trends and attack patterns. And CyStack converts it into short and helpful notes for your reference.
Check them out now!
Key Statistics on 2022 Trends of Cyber Threats
If you are in a hurry, quickly save the key statistics and highlights here for further planning:
- Most attack type is Ransomware: Despite decreasing from 23% to 21% in cases last year, Ransomware is still the top attack type. REvil has made up 37% of all ransomware-related attacks.
- Most targeted industry is manufacturing: It is not financial services but manufacturing as the current top attacked industry.
- Most attacked geography is Asia: 26% of all attacks target the victims in Asia in their crosshairs.
- 3 most phished brands: Microsoft, Apple, and Google, are the top three targetted by criminals.
- 3 most dangerous threat groups: Meanwhile, the top three active criminals are ITG17 (MuddyWater), cybercriminal group ITG23 (Trickbot), and Hive0109 (LemonDuck.)
- 41% of incidents are caused by exploiting phishing: Phishing operations are considered the top pathway to compromise and gain initial access.
- 3X more effective when it comes to phone calls: Vishing or voice phishing nets a click from 53.2% of victims, which is three times more effective than traditional phishing.
- 146% is the increase in Linux ransomware using new code: It is indicated that there is a Linux ransomware innovation.
- 61% of incidents have happened at OT-connected organizations: Criminals now usually compromise OT-connected organizations, of which 36% of attacks are Ransomware.
- 2,204% increase in reconnaissance against OT: Attackers succeed in more SCADA Modbus OT devices reconnaissance accessible via the internet.
2022 Top Attack Types
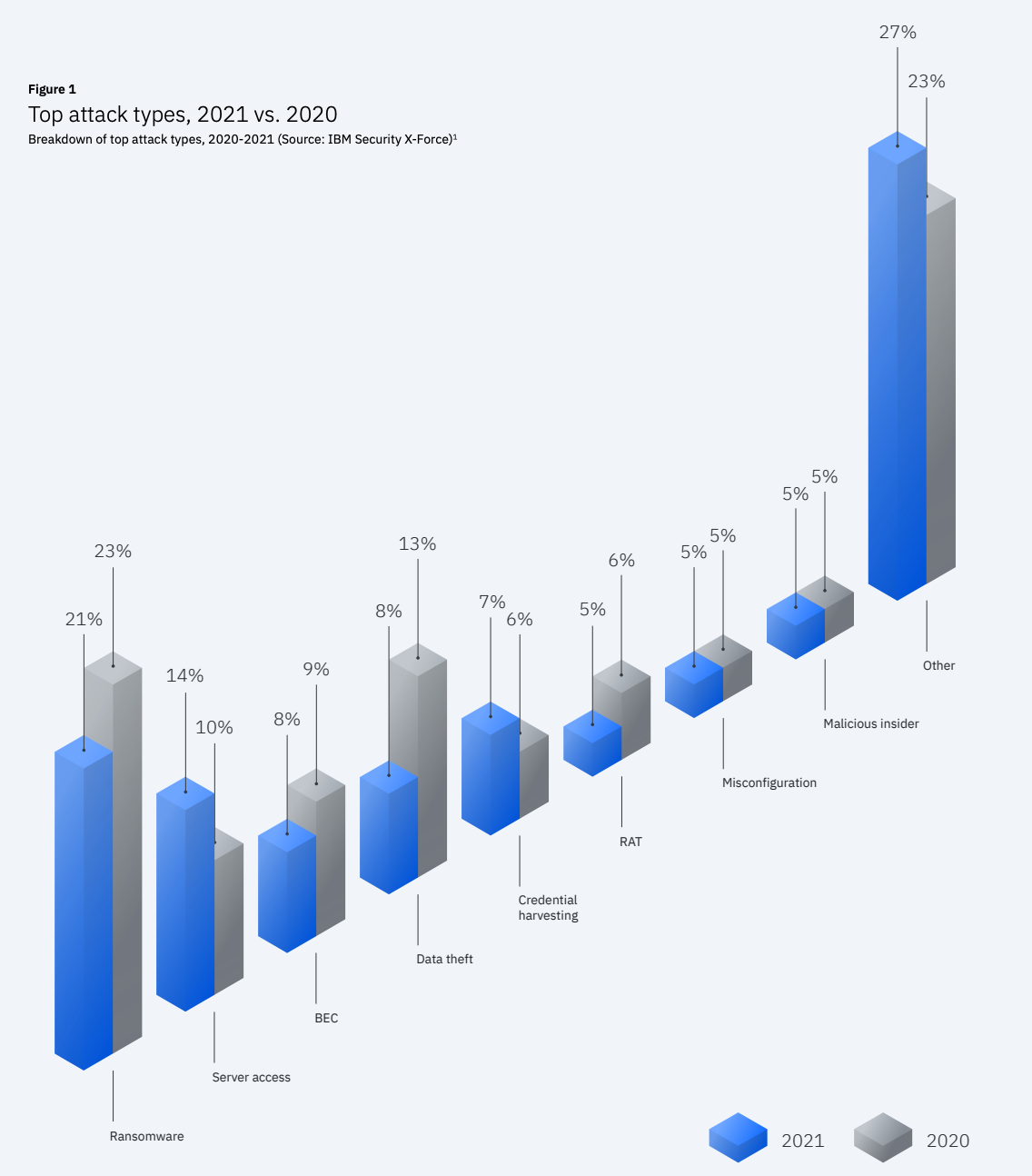
Attacks are not all the same, but they differ from the initial infection vectors. IBM categorizes those attacks by types, including Ransomware, server access, business email compromise (BEC), data theft, credential harvesting, remote access trojans (RAT), misconfiguration, malicious insider, etc.
The top four attack types in 2022 are Ransomware, server access, and BEC.
Ransomware
Ransomware has been the most common attack type detected for three years in a row. 2022 will be no exception. In addition, May and June annually witness a higher frequency of attacks.
The number of ransomware cases also appears to decrease due to the shutdown of several groups. Those groups usually spring up and rebrand within 17 months – on average, against the arresting threats or law enforcement’s actions. However, some temporarily shut down and continued their operations under new names.
IBM alerts on a new trend in Ransomware: “triple extortion.” Accordingly, attackers make two malicious attacks, demanding money from both initial victims and anyone who the disclosure of data leakage might impact.
Server access
In server access, criminals gain unauthorized access to a server and further exploit vulnerabilities. This type made up 11% of all incidents last year and among 2022 trends of cyber threats.
Threat actors usually cause an initial server access attack by employing penetration testing tools or deploying malware on a server. Or, they can exploit a known vulnerability to allow remote code execution on the server.
Business email compromise (BEC)
Ranking in the third place of 2022 top attack types, BEC attacks still decrease in cases due to widespread multifactor authentication (MFA) solutions.
As a result, attackers tend to switch to geographies such as Latin America or North America, where MFA is not widely applied.
2022 Top Infection Vectors
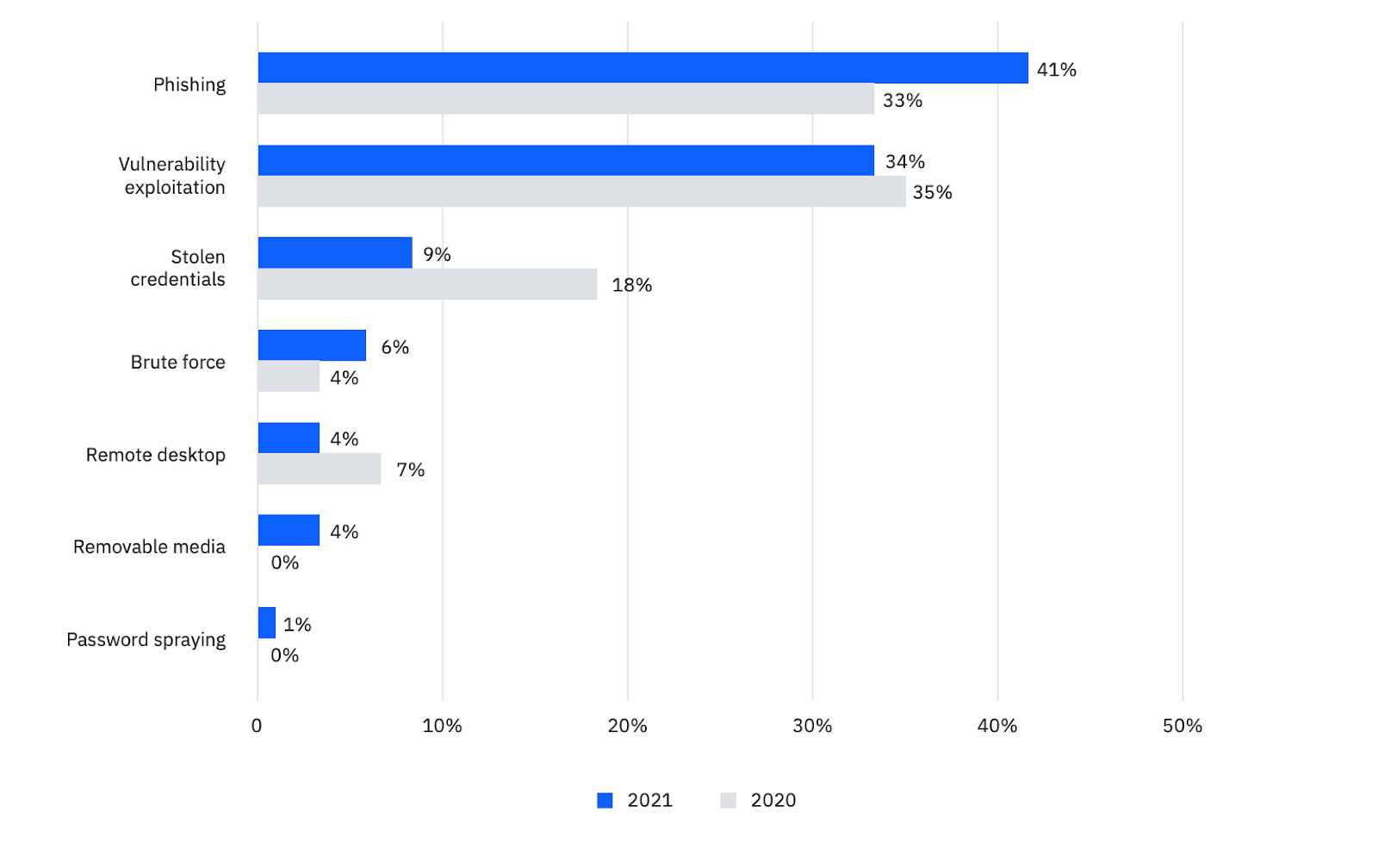
Why care about top infection vectors? – They are paths that attackers use to exploit cybersecurity vulnerabilities. When you are well aware of those vectors, you can avoid getting involved with them in the first place.
So far, the top three infection vectors are phishing, vulnerability exploitation, and IoT and OT assets as well mentioned in the key statistics on 2022 trends of cyber threats.
Phishing
Phishing was witnessed in 41% of cyber attacks, making it the top infection vector for the time being. The average click rate was 17.8% and rose to 53.2% when adding vishing and voice phishing. Of all phishing tactics, conducting social engineering penetration testing attacks through emails is common.
The report of IBM also revealed the top brands frequently spoofed in phishing kits. They are almost all large financial institutions and technology companies, such as Microsoft, Apple, Google, BMO Harris Bank, Chase, Amazon, Dropbox, DHL, CNN, Hotmail, and Facebook.
Read more: How Does Big Tech Invest In Cybersecurity?
Vulnerability exploitation
Vulnerability exploitation used to be the top infection vector in 2022. In 2021 and onwards, this vector remains in the top three.
Attackers target vulnerabilities to access victims’ networks to run further operations. To do so, they will first leverage multiple known vulnerabilities, such as CVE-2021-35464, CVE-2019-19781, or the Log4j vulnerability CVE-2021-44228.
It is worth knowing that vulnerabilities related to the internet of things (IoT), industrial control systems (ICS), and by extension, operational technology (OT) increase annually. This opens paths for attackers to exploit your networks. It is a trade-off for the power of internet protocols and digitization.
2022 Trends in Malware Development

With the above top attack types and the top infection vectors in mind, threat actors have made endless efforts to innovate their malware to be more capable and harder to detect across operating systems.
Next-level detection evasion
Criminals now use different encryption techniques to bypass host-based detection systems, such as intermittent encryption, sophisticated packing and code obfuscation, and command and control (C2) communications.
Malware authors even employ different programming languages to increase the difficulty of reverse engineering.
Malware focuses on Docker.
Many cybercriminals such as XorDDoS, Tsunami, or Groundhog switch to attack Docker containers commonly used in Platform-as-a-service cloud packages. This development highlighted the crypto miners, malicious activity of IoT malware, and other malware strains to leverage their mining power.
Ransomware focus on ESXi
In addition to Docker containers, ransomware families also target VMWare ESXi servers and encrypt the virtual machine files instead of infecting the operating systems, considering the increasing use of virtualization.
Some known threat groups using this method are BlackMatter, REvil, Babuk, and HelloKitty.
Nim is in
Besides the top-chosen Golang in 2020, attackers have adopted an additional programming language – Nim.
The language compiles the Nimar backdoor and Zebrocy – a Russian malware.
Linux threats
Linux remains in the most interest of threat actors because malware is dramatically targeting Linux environments. Such a trend attributes to organizations moving into Linux-rely cloud environments.
Even worse, Linux malware innovates by adding unique variations to the code, observed in Ransomware, banking, trojans, etc.
Threat actors target cloud environments.
As seen in the Linux trend, threat actors now shift their targeting into cloud environments for nearly a quarter of attacks. API misconfiguration vulnerabilities involve two-thirds of the cases.
That said, organizations must maintain hardened systems, ensure policy compliance, and enact effective password policies as best practices.
Fileless malware in the cloud
Fileless malware usually exploits legitimate scripting languages and signatures to lurk in memory and elude standard detection tools. Moreover, cybercriminals even advance their actions by using Ezuri – a memory loader and VermillionStrike – a penetrating testing tool, to launch their undetected malware.
2022 Cyber Threats Geographic Trends
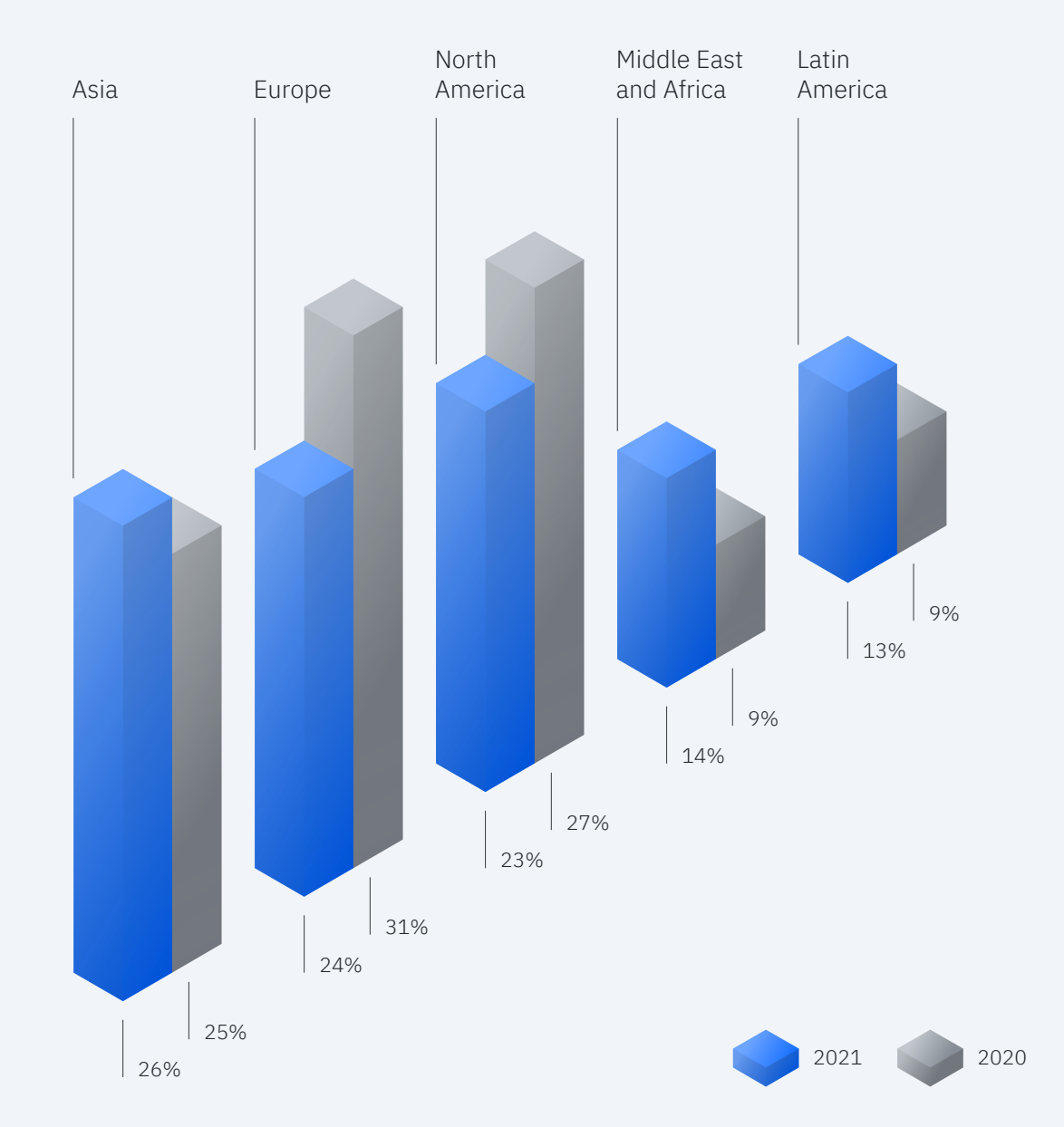
Asia
Asian organizations and individuals, including those from Australia, India, East and Southeast Asia, and the Pacific Islands, are the most targeted.
- Server access attacks: 20%
- Ransomware: 11%
- Data theft: 10%
- Remote access trojans: 9%
Finance and insurance industries have made up 30% of incidents, closely followed by manufacturing (29%), professional and business services (13%), and then transportation (10%). By countries, Japan, Australia, and India are the most frequently attacked.
Europe
IBM only surveyed organizations in Eastern Europe, Western Europe, and Turkey. Those organizations suffer from 24% of global attacks.
- Ransomeware: 26%
- Server access: 12%
- Data theft: 10%
- Misconfiguration: 8%
- Malicious insider: 6%
- Fraud: 6%
Threat attackers usually pursue “big game hunting” as they target vulnerability exploitation of large and wealthy corporations to achieve a big ransom payout.
Manufacturing, finance, and insurance are the top attacked industries, making up 25% and 18%, respectively. Professional and business services rank third place at 15%. Meanwhile, the U.K, Italy, and Germany are reported as the most-attacked European countries.
North America
When we mention North American countries, we include the U.S and Canada. In these countries, Ransomware remains the top attack type.
- Ransomware: 30%
- BEC: 12%
- Server access: 9%
It is worth taking notes of the most frequently used attack vectors, namely, phishing (47%), vulnerability exploitation (29%), removable media (12%), brute force (9%), and stolen credentials (9%).
In terms of industry, manufacturing was the top vulnerable industry, followed by professional and business services, retail and wholesale.
2022 Industry Trends of Cyber Threats
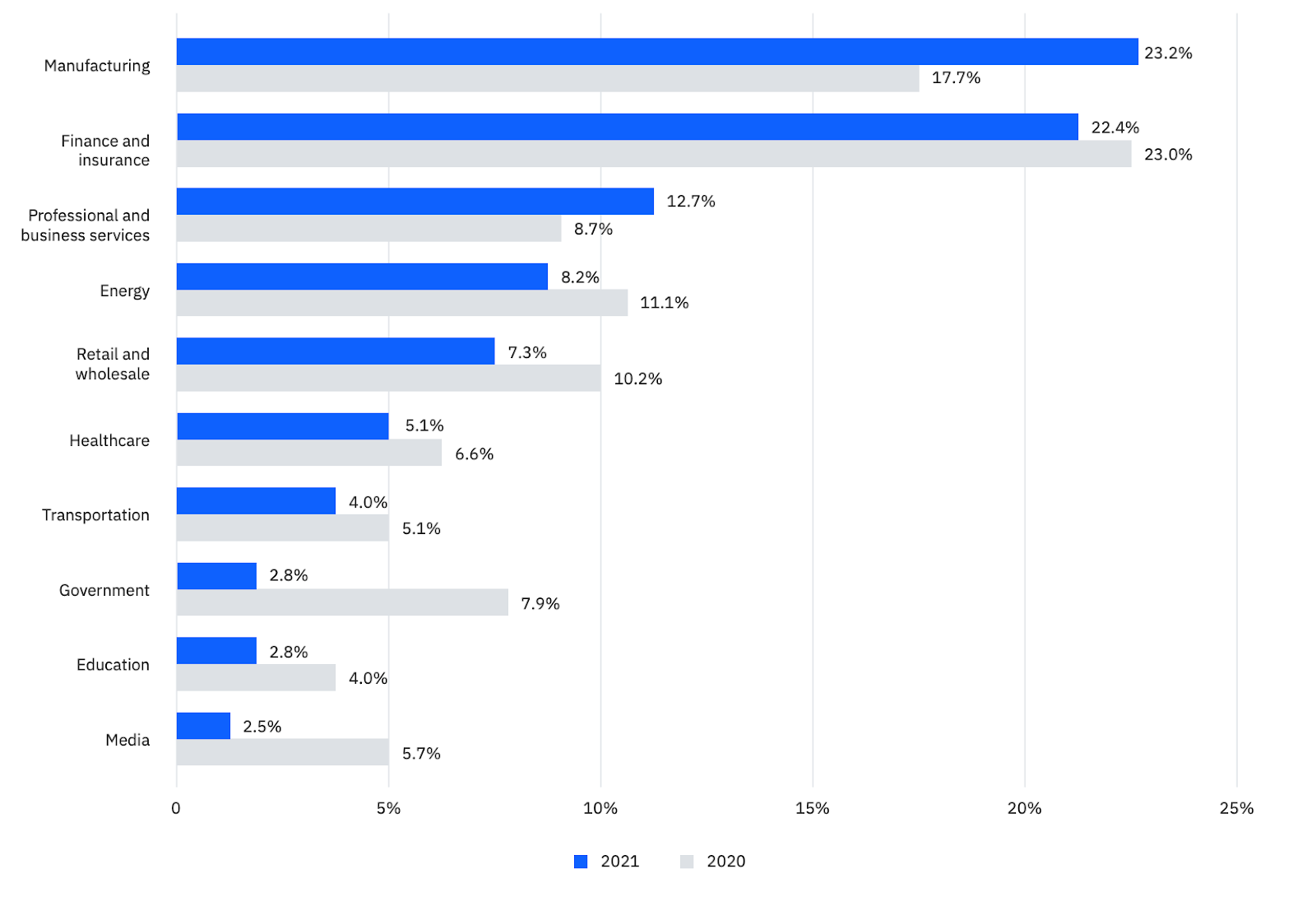
Manufacturing
Manufacturing was the most attacked industry, targeted at 23.2%. Nearly 32% of those attacks have occurred in Asia, followed by North America (27%) and Europe (26%).
- Ransomware: 23%
- Server access; 12%
- BEC: 10%
- Data theft: 10%
Vulnerability exploitation and phishing, meanwhile, are the top infection vectors in manufacturing industries. Thus, organizations must devote their effort to detecting phishing threats further and enhancing vulnerability management.
Also check: Top 9 Best Cybersecurity Tips For Leaders
Finance and insurance
Asia (34%) and the Middle East, and Africa (29%) saw a high volume of attacks in the finance and insurance industry, whereas Europe (19%), Latin America (9%(, and North America (9%) together share small attack percentage.
- Server access: 14%
- Ransomware: 10%
- Misconfigurations: 10%
- Fraud: 10%.
Despite adopting high standards and improved security practices, the industry is still vulnerable to phishing (46%), vulnerability exploitation (31%), password spraying, VNP access, and brute force.
Professional and business services
Professional services refer to law firms, technology providers, specialist consultants, etc., while business services include human resources, office administration, security, travel, and more. Together, they are categorized into the professional and business services industry.
- Ransomware: 32%
- Server access: 19%
- Malicious insiders: 13%
Regarding threat vectors, vulnerability exploitation makes up 50%, with phishing and stolen credentials accounting for another 20% each. Multiple vulnerability exploitation was usually involved in the Microsoft Exchange vulnerabilities published in 2021.
Wrapping Up: Experts’ Risk Mitigation Recommendations
Since cyber threats have been increasing in cases and are more complicated in properties, IBM revealed helpful security principles to combat them effectively!
- Develop a response plan for Ransomware using security automation
- Adopt multifactor authentication to accept remote access points into a network
- Adopt a layered approach to combat phishing
- Refine and mature your vulnerability management system
- Conduct frequent and extended detection and response to be proactive over attackers
 7 minutes read
7 minutes read
