Many people doubt the blockchain government!
Theoretically, the technology is supposed to provide an ironclad and truthless distributed ledger. No particular parties or individuals can govern your transactions within the chains.
However, people still suspect such transparency and self-government, wondering whether those taking responsibility for the blockchain projects or networks, such as founders and developers, can control the operation of the blockchain and cheat the users.
Is the suspicion correct? Find the answer in this article.
Main Characteristics of Blockchain Transactions

According to the famous multinational technology corporation IBM, blockchain supports improved security, transparency, and instant traceability over transactions.
- Decentralized distributed ledger
Blockchain uses Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), an infrastructure of protocols and smart contracts that allow accessing, validating and recording data transactions simultaneously and immutably without intermediaries.
All data updated are distributed across nodes, then.
- Improved security
Both personal and business data are sensitive and vulnerable to exploitation. Thus, it is essential to manage how those data are viewed.
Using blockchain, you can encrypt the data into blocks and give permissions to particular parties. They can view the information and add new blocks of data to the chain; however, parties cannot edit or delete the existing blocks. That way, your data are secure against unauthorized access and any damaging attempt.
Even in the case of a one-in-a-million attack, your data are still secure and backed up quickly. This is a benefit of decentralized distribution networks when damages in a node will not affect other nodes.
Read more: Is blockchain secure?
- Enhanced transparency
In a traditional centralized network, each stakeholder keeps their database, making it time-consuming to inform stakeholders of changes.
Meanwhile, blockchain government is peer-to-peer, meaning all chain participants simultaneously get the same blocks.
- Instant traceability
Better transparency enables users to audit an asset anytime if needed.
Accordingly, each data transaction is encrypted and stamped with a specific date and time. Thus, the owner of the blocks can check the history and spot any fraud.
How Does Blockchain Government Work?

Components of a Blockchain
A blockchain often contains five components: nodes, ledgers, wallets, nonces, and hashes.
- Nodes
There are two node types: full and partial.
The full node maintains a complete transaction copy; thus, it can validate, accept, or deny additional transactions.
Meanwhile, a partial node only contains the hash value. This node is lightweight enough for low computational power and storage capacity.
- Ledgers
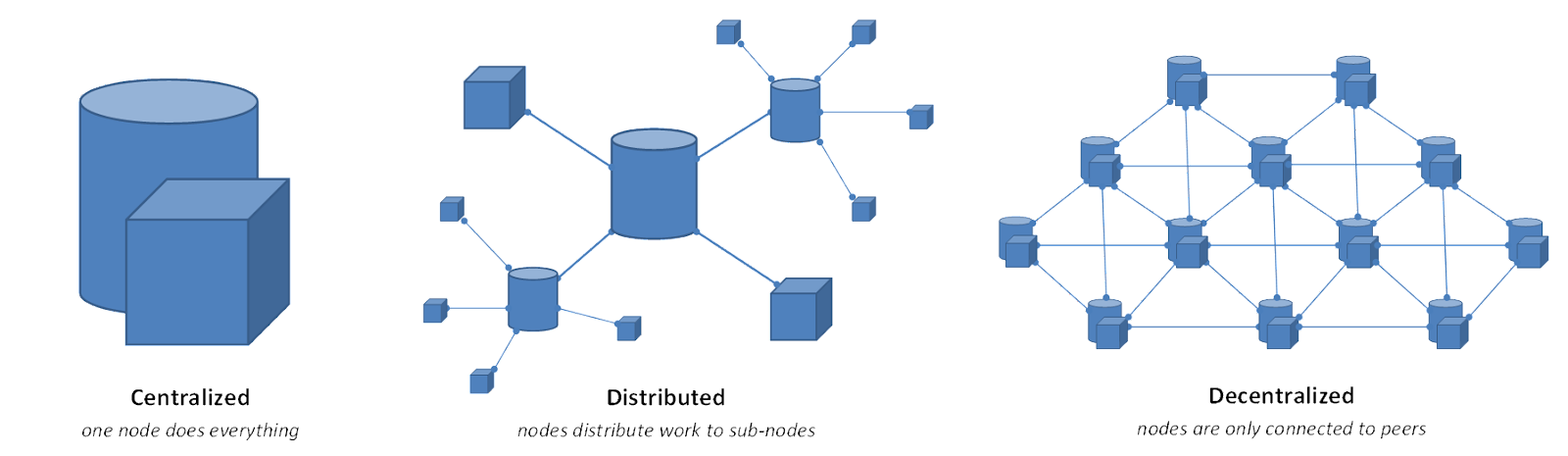
Ledgers refer to a digital database that allows exchanging cryptocurrencies between different nodes. Those ledgers can be centralized, distributed, or decentralized.
- Wallets
Wallets are places to store digital cryptocurrencies, ready to exchange. They can be either hot or cold wallets.
Hot wallets are connected to the internet so the owners can make day-to-day transactions. In contrast, cold wallets are paper or hardware usable without the internet.
- Nonces
The nonce is the short form for the concept “number only used one.” Whenever a node adds a new block or validates a transaction, the chain randomly generates a 32-bit number to secure the transaction.
Hackers might do guesswork to discover the nonce of a hash and penetrate the blockchain. Yet, this is extremely rare and requires significant trials and errors.
- Hash
Each block has a specific size, defined by a hash. When the block uses up its available hash capacity, the remaining information saves for another transaction.
How to Govern and Control Transactions in Blockchain?
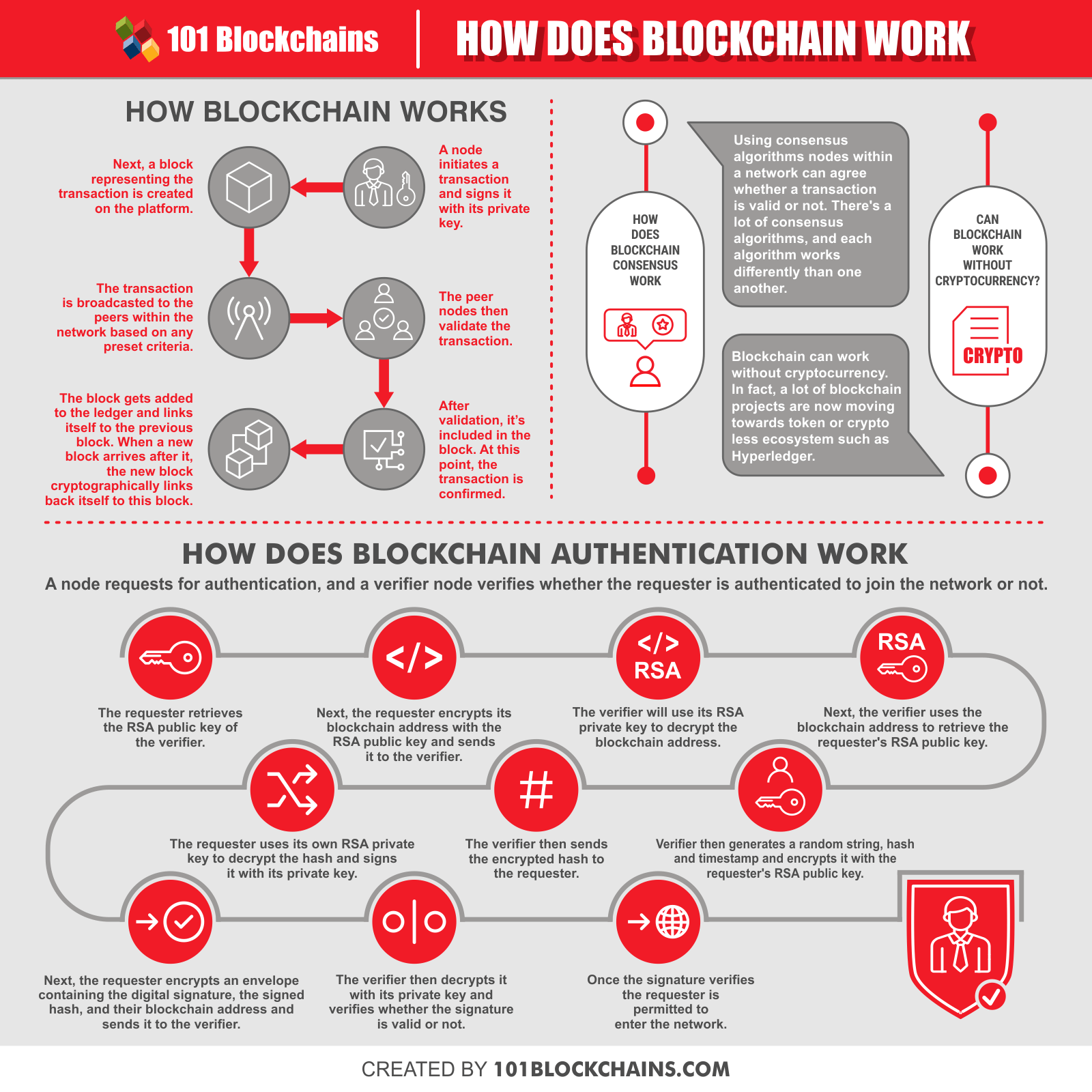
The diagram of 101Blockchains above describes a typical flow a blockchain will govern and control its transactions.
- At first, a node initiates a transaction, including data, validation rules, etc. and signs the transaction with a private key.
- Then, the chain determines a containing block for the new marketing, usually via a flooding protocol.
- Other dedicated nodes in the network get the broadcast of the new transaction, as well.
- Next, those nodes start to validate the transaction using preset conditions, known as smart contracts.
- The containing block will be recorded in the ledger with a timestamp if the transaction is valid.
- In the end, such a newly-created block creates a hash pointer to link itself to the previous blocks in the chain.
Wrapping Up
Our article gives a detailed answer to “How is blockchain governed and controlled?”
That being said, validating and adding a new block process is automatic without the interference of any other parties or individuals.
In other words, blockchain transactions are secure and transparent to use. If there is anything that still makes you concerned, feel free to leave us a comment here for further consultation.
 4 minutes read
4 minutes read
