Hôm nay, chúng ta sẽ tìm hiểu về đăng nhập và đăng xuất với Spring Security. Trước khi làm theo ví dụ này, đầu tiên bạn nên xem qua bài viết trước của chúng tôi về framework này để nắm được các kiến thức cơ bản.

Ví dụ về đăng nhập và đăng xuất với Spring Security
Trong bài viết này, chúng ta sẽ phát triển một ứng dụng web Spring 4 MVC Security với tính năng đăng nhập và đăng xuất bằng cách sử dụng tùy chọn In-Memory. Ví dụ này sử dụng Spring Java Config cùng với các Spring Annotation. Điều này có nghĩa là ta sẽ không cần dùng đến file web.xml và cấu hình Spring bằng XML như cách cũ.
Spring 4 Security Module hỗ trợ các tùy chọn sau để lưu trữ và quản lý thông tin xác thực người dùng (user credential):
- In-Memory Store (lưu trữ trong bộ nhớ)
- Cơ sở dữ liệu quan hệ (RDBMS)
- Kho dữ liệu NoSQL
- LDAP
Trong ví dụ này, ta sẽ sử dụng tùy chọn In-Memory Store. Các tùy chọn khác sẽ được đề cập trong những bài viết sau. Trong ví dụ này, chúng ta sẽ sử dụng Spring 4.0.2.RELEASE, Spring STS 3.7 Suite IDE, Spring TC Server 3.1 với Java 1.8 và công cụ build Maven.
Ví dụ đăng nhập với Spring Security
Chúng ta sẽ phát triển logic đăng nhập và đăng xuất bằng các tính năng của Spring 4 Security. Mục tiêu chính của ứng dụng này là phát triển một ứng dụng mà không cần sử dụng web.xml và không cần viết một dòng cấu hình Spring Bean bằng XML nào. Điều này có nghĩa là chúng ta sẽ sử dụng tính năng Spring Java Config với các Spring Annotation.
Ứng dụng sẽ có các tính năng sau:
- Trang Chào mừng (Welcome Page)
- Trang Đăng nhập (Login Page)
- Trang Chủ (Home Page)
- Tính năng Đăng xuất (Logout)
Hãy làm theo các bước sau để phát triển và tìm hiểu tính năng đăng nhập đơn giản trong Spring 4 Security.
Tạo một project “Simple Spring Web Maven” trong Spring STS Suite với các thông tin sau
Project Name : SpringMVCSecruityMavenApp
Cập nhật file pom.xml với nội dung dưới đây
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project
xsi:schemaLocation="<https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0>
<https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd>"
xmlns="<https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0>"
xmlns:xsi="<https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance>">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.journaldev</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringMVCSecruityMavenApp</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>1.0</version>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring.version>4.0.2.RELEASE</spring.version>
<spring.security.version>4.0.2.RELEASE</spring.security.version>
<servlet.api.version>3.1.0</servlet.api.version>
<jsp.api.version>2.2</jsp.api.version>
<jstl.version>1.2</jstl.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-web</artifactId>
<version>${spring.security.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-config</artifactId>
<version>${spring.security.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>${servlet.api.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>${jsp.api.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>jstl</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>${jstl.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>SpringMVCSecruityMavenApp</finalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>${java.version}</source>
<target>${java.version}</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<failOnMissingWebXml>false</failOnMissingWebXml>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
LƯU Ý: Nếu bạn không hiểu rõ về cờ <failOnMissingWebXml>, hãy đọc phần cuối của bài viết này để biết cách sử dụng của nó.
Đầu tiên, phát triển Login Controller bằng annotation @Controller của Spring.
File LoginController.java:
package com.journaldev.spring.web.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@RequestMapping(value = { "/"}, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView welcomePage() {
ModelAndView model = new ModelAndView();
model.setViewName("welcomePage");
return model;
}
@RequestMapping(value = { "/homePage"}, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView homePage() {
ModelAndView model = new ModelAndView();
model.setViewName("homePage");
return model;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/loginPage", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView loginPage(@RequestParam(value = "error",required = false) String error,
@RequestParam(value = "logout", required = false) String logout) {
ModelAndView model = new ModelAndView();
if (error != null) {
model.addObject("error", "Invalid Credentials provided.");
}
if (logout != null) {
model.addObject("message", "Logged out from JournalDEV successfully.");
}
model.setViewName("loginPage");
return model;
}
}
Ở trên ta đã định nghĩa ba phương thức trong LoginController để xử lý ba loại request khác nhau từ client:
welcomePage()sẽ xử lý tất cả request của client có URI là/.homePage()sẽ xử lý tất cả request của client có URI là/homePage.loginPage()sẽ xử lý tất cả request của client có URI là/loginPage.- Trong
loginPage(), chúng ta đã xử lý các thông báo lỗi và đăng xuất.
- Tiếp theo, viết class
LoginSecurityConfigđể cung cấp các tính năng bảo mật cho việc đăng nhập và đăng xuất với Spring 4 Security API.
File LoginSecurityConfig.java:
package com.journaldev.spring.secuity.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class LoginSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
public void configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder authenticationMgr) throws Exception {
authenticationMgr.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("journaldev")
.password("jd@123")
.authorities("ROLE_USER");
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/homePage").access("hasRole('ROLE_USER')")
.and()
.formLogin().loginPage("/loginPage")
.defaultSuccessUrl("/homePage")
.failureUrl("/loginPage?error")
.usernameParameter("username").passwordParameter("password")
.and()
.logout().logoutSuccessUrl("/loginPage?logout");
}
}
Chúng ta đã định nghĩa hai phương thức trong LoginSecurityConfig ở file trên để lưu trữ, quản lý thông tin xác thực người dùng và xử lý các tính năng bảo mật đăng nhập và đăng xuất.
- Annotation
@EnableWebSecurityđược dùng để kích hoạt tính năng bảo mật web trong bất kỳ ứng dụng web nào. - Annotation
@EnableWebMVCSecurityđược dùng để kích hoạt tính năng bảo mật web trong ứng dụng web dựa trên Spring MVC. LƯU Ý:@EnableWebSecurity=@EnableWebMVCSecurity+ các tính năng bổ sung. Đó là lý do tại sao Annotation@EnableWebMVCSecuritychuẩn bị bị loại bỏ trong Spring Framework 4.x. ClassLoginSecurityConfig(hoặc bất kỳ class nào được chỉ định để cấu hình Spring Security) nên kế thừa từ classWebSecurityConfigurerAdapterhoặc triển khai interface liên quan. - Phương thức
configureGlobal()được sử dụng để lưu trữ và quản lý thông tin xác thực người dùng. - Trong phương thức
configureGlobal(), ta có thể sử dụng phương thứcauthorities()để định nghĩa các role của ứng dụng như“ROLE_USER”. Ta cũng có thể sử dụng phương thứcroles()cho cùng mục đích. - Sự khác biệt giữa phương thức
authorities()vàroles():authorities()cần một tên role hoàn chỉnh như“ROLE_USER”, trong khiroles()chỉ cần tên role như“USER”. Nó sẽ tự động thêm tiền tố“ROLE_”vào tên role“USER”. LƯU Ý: Chúng ta sẽ phát triển một ví dụ khác để minh họa các role như“USER”,“ADMIN”trong các bài viết sắp tới. - Phương thức quan trọng để xử lý bảo mật Đăng nhập và Đăng xuất là
configure(HttpSecurity http). - Đoạn code sau được sử dụng để ngăn chặn truy cập trái phép vào
/homePage. Nếu cố gắng truy cập trang này, bạn sẽ tự động được chuyển hướng đến trang/loginPage.
.antMatchers("/homePage").access("hasRole('ROLE_USER')")
Nếu ta bỏ đi lời gọi phương thức access(“hasRole(‘ROLE_USER’)”), thì ta có thể truy cập trang này mà không cần đăng nhập vào ứng dụng. Chúng ta đã cấu hình các tính năng đăng nhập và đăng xuất bằng các phương thức formLogin() và logout().
Kích hoạt cấu hình Spring MVC với file LoginApplicationConfig.java:
package com.journaldev.spring.secuity.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView;
@EnableWebMvc
@Configuration
@ComponentScan({ "com.journaldev.spring.*" })
@Import(value = { LoginSecurityConfig.class })
public class LoginApplicationConfig {
@Bean
public InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver() {
InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
viewResolver.setViewClass(JstlView.class);
viewResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/views/");
viewResolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
return viewResolver;
}
}
Ở đây ta sử dụng class LoginApplicationConfig để định nghĩa các View Resolver (thành phần xác định view nào sẽ render dữ liệu từ controller) của Spring MVC và tránh việc phải viết file web.xml.
- Annotation
@EnableWebMvcđược dùng để kích hoạt các tính năng của ứng dụng Spring Web MVC trong Spring Framework. - Annotation
@Importđược dùng để import class cấu hình Spring Security vào class này. - Annotation
@ComponentScanđược dùng để quét các thành phần trong package đã chỉ định. Nó tương đương với<context:component-scan>trong cấu hình Spring XML.
Khởi tạo Spring Security với đoạn code sau:
package com.journaldev.spring.secuity.config.core;
import org.springframework.security.web.context.AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer;
public class SpringSecurityInitializer extends AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer {
}
SpringSecurityInitializer được dùng để đăng ký springSecurityFilterChain. Điều này giúp không cần phải viết cấu hình Filter trong file web.xml.
Khởi tạo ứng dụng Spring MVC trong file SpringMVCWebAppInitializer.java dưới đây. Class SpringMVCWebAppInitializer được sử dụng để khởi tạo DispatcherServlet mà không cần file web.xml khi cấu hình dựa trên Annotation.
package com.journaldev.spring.secuity.config.core;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
import com.journaldev.spring.secuity.config.LoginApplicationConfig;
public class SpringMVCWebAppInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[] { LoginApplicationConfig.class };
}
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return null;
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] { "/" };
}
}
LƯU Ý:
- Khi chúng ta truy cập ứng dụng, theo mặc định, phương thức
getServletMappings()củaSpringMVCWebAppInitializersẽ cho phép truy cập URL gốc:/. Chúng ta có thể ghi đè phương thức này để chuyển hướng đến một URL khác. - Đội ngũ team Spring (Pivotal) đang xử lý vấn đề này để giảm bớt lượng code Java cần thiết bằng cách giới thiệu một annotation mới.
Tạo file welcomePage.jsp
<h3>Welcome to JournalDEV Tutorials</h3>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/loginPage">Login to Journal</a>
Tạo file loginPage.jsp
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="<https://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core>"%>
<html>
<body onload='document.loginForm.username.focus();'>
<h3>JournalDEV Tutorials</h3>
<c:if test="${not empty error}"><div>${error}</div></c:if>
<c:if test="${not empty message}"><div>${message}</div></c:if>
<form name='login' action="<c:url value='/loginPage' />" method='POST'>
<table>
<tr>
<td>UserName:</td>
<td><input type='text' name='username' value=''></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Password:</td>
<td><input type='password' name='password' /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan='2'><input name="submit" type="submit" value="submit" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
<input type="hidden" name="${_csrf.parameterName}" value="${_csrf.token}" />
</form>
</body>
Tạo file homepage.jsp
<%@taglib prefix="c" uri="<https://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core>"%>
<h3>Welcome to JournalDEV Tutorials</h3>
<ul>
<li>Java 8 tutorial</li>
<li>Spring tutorial</li>
<li>Gradle tutorial</li>
<li>BigData tutorial</li>
</ul>
<c:url value="/logout" var="logoutUrl" />
<form id="logout" action="${logoutUrl}" method="post" >
<input type="hidden" name="${_csrf.parameterName}" value="${_csrf.token}" />
</form>
<c:if test="${pageContext.request.userPrincipal.name != null}">
<a href="javascript:document.getElementById('logout').submit()">Logout</a>
</c:if>
Cấu trúc cuối cùng của project sẽ trông như sau:
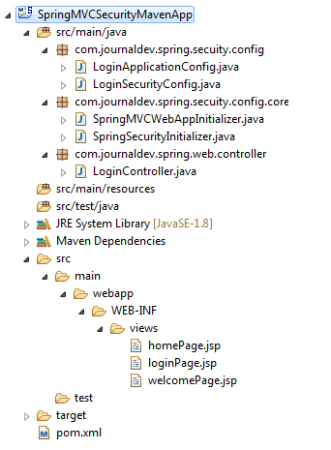
Chạy ví dụ đăng nhập và đăng xuất với Spring Security MVC
Để chạy ứng dụng Spring Web này, chúng ta cần một Web Container bất kỳ hỗ trợ môi trường Spring 4 và Java 8 với Servlet 3.1.0 Container.
Deploy và chạy trên server Spring TC trong Spring STS Suite. Nó sẽ tự động truy cập trang chào mừng như bên dưới.
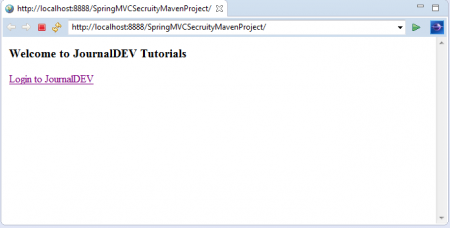
Nhấn vào liên kết Login to JournalDEV để truy cập trang đăng nhập.
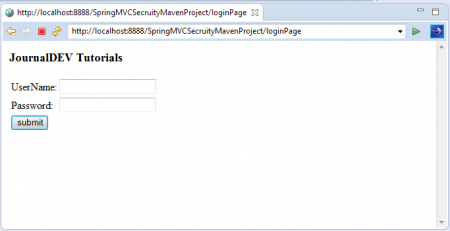
Bây giờ, hãy thử nhập thông tin đăng nhập sai và nhấn nút Login.
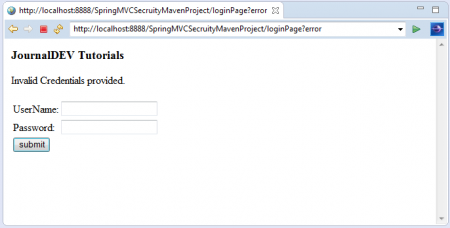
Ta sẽ thấy thông báo lỗi: “Invalid Credentials provided.” Nhập lại thông tin đăng nhập chính xác đã được cấu hình trong class LoginSecurityConfig.
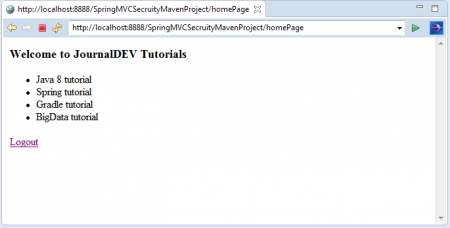
Khi đăng nhập thành công, ta sẽ thấy trang chủ của ứng dụng cùng với link Logout. Nhấn vào link Logout để đăng xuất khỏi ứng dụng.
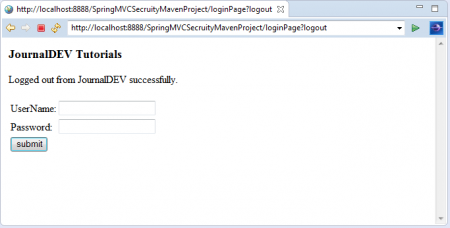
Ta sẽ thấy ứng dụng đã đăng xuất thành công kèm theo thông báo và chuyển hướng về lại trang đăng nhập.
LƯU Ý: Nếu để ý, bạn sẽ thấy ví dụ này ta không sử dụng file web.xml. Vì đây là một ứng dụng web, Maven sẽ tìm kiếm file web.xml và báo lỗi nếu không tìm thấy nó trong ứng dụng. Để tránh các vấn đề liên quan đến Maven, chúng ta cần cấu hình cờ <failOnMissingWebXml> trong file pom.xml.
Tổng kết
Trên đây là toàn bộ nội dung về cách tạo một ví dụ về đơn giản đăng nhập và đăng xuất với Spring Security. Trong các bài viết tiếp theo, chúng ta sẽ tìm hiểu thêm một số ví dụ khác không kém thực tế và hữu ích như quản lý Role, tính năng Remember-Me, và WebSocket Security.
 8 phút để đọc
8 phút để đọc
